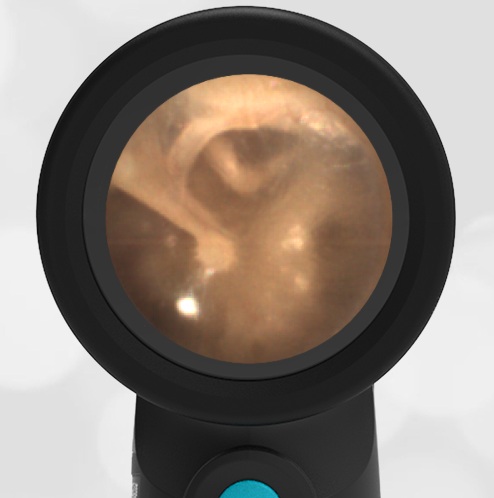
Normal Ear Drum Features
A routine physical exam of a healthy 25-year-old female reveals this image of her left ear drum taken with the WiscMed Wispr Digital Otoscope.
Can you identify at least three anatomical features found in this image?

It’s easy to identify the three bones of the middle ear, the malleus, the incus and the stapes. These are often referred to as the hammer, anvil and stirrup. These three bones transmit the motion of the ear drum to the inner ear where special hair sensors suspended in fluid send electrical signals to our brain that we interpret as hearing.
The cone of light is caused by reflected light from the Wispr otoscope. It is in the anterior-inferior portion of the ear drum with the apex of the cone originating at the umbo of the malleus. The chorda tympani nerve has nothing to do with hearing. It “borrows” the middle ear space to find its way to the posterior of the mouth where it provides innervation for salivation and taste. The promontory is part of the inner ear cochlear apparatus that provides for balance. Here are the complete video exams of the left and right ears.




