Visual Ear Diagnosis Guide
There are a number of ear conditions that are commonly found in clinic. This article presents six of the most common conditions seen in the primary clinic. Included are images of the condition, typical presenting history and annotated diagnostic features.
Normal Ear

Typical History: Healthy patient with no ear complaints and no history of ear infections or trauma

Diagnostic Features: Malleus is easily appreciated. Light reflex is present. No bulging of the ear drum. Each ear is different and not all landmarks are visible in all ears.
Erythema (redness)

Typical History: Crying child

Diagnostic Features: Common finding in a crying child that is not happy to be at clinic. Often confused with an infection if too brief a view is obtained.
Myringosclerosis (sclerosis)

Typical History: Patient with history of ear infections or ear tubes.

Diagnostic Features: Myringoclerosis is calcium and phosphate depositions in the middle layer of the ear drum. Does not generally affect hearing. No treatment indicated.
Otitis Media with Effusion (OME)

Typical History: Several days of viral symptoms without significant ear pain. May have a sensation of ear pressure.

Diagnostic Features: No bulging. Air-Fluid levels indicate Eustachian tube is functioning properly. Antibiotics not indicated.
Acute Otitis Media (AOM)

Typical History: Several days of viral symptoms followed by developing ear pain and decreased hearing.

Diagnostic Features: Often described as an angry donut. Because of the bulging, no landmarks are visible. Easily appreciated as abnormal. Antibiotics should be considered.
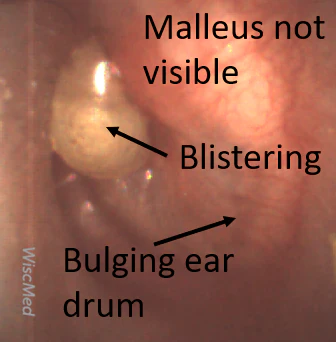
Bullous Myringitis

Typical History: Several days of viral symptoms followed by significant ear pain and decreased hearing

Diagnostic Features: Considered a severe case of AOM. Angry donut with blisters. Often quite painful. Antibiotics are generally indicated.
